In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, one innovation has been capturing the imagination of both tech enthusiasts and the general public alike: self-driving cars. These autonomous vehicles, often seen as a futuristic concept, are rapidly becoming a reality that promises to revolutionize transportation as we know it. This blog post delves into the world of self-driving cars, exploring their technology, benefits, challenges, and the road ahead.
Table of Contents
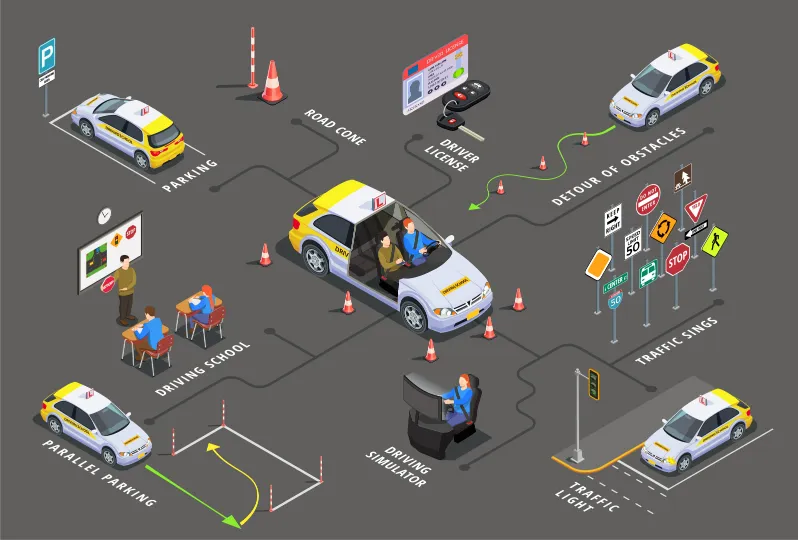
What is Self-Driving Car Technology?
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles or driverless cars, are automobiles equipped with advanced technology that allows them to navigate and operate without human intervention. This technological marvel is considered by many as the next major leap in the realm of transportation and technology.
How Self-Driving Cars Work
Technology Behind the Magic
Self-driving cars rely on a complex combination of sensors, cameras, Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging), and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to perceive their environment. These vehicles can interpret road conditions, traffic signs, and the movement of other vehicles, making real-time decisions to navigate safely.
Levels of Automation
Autonomous vehicles are categorized into different levels of automation, ranging from partial automation, where the driver still needs to be engaged, to fully autonomous, where the vehicle handles all aspects of driving without human intervention.
Benefits of Self-Driving Cars
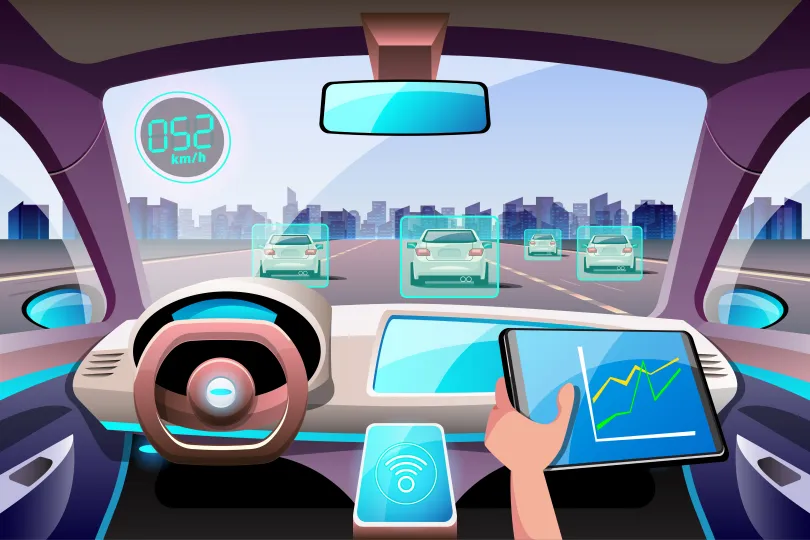

Enhanced Safety
One of the most compelling arguments for self-driving cars is their potential to drastically reduce accidents. Autonomous vehicles, with their lightning-fast reaction times and ability to monitor the surroundings 360 degrees, are expected to make our roads significantly safer.
Improved Traffic Flow
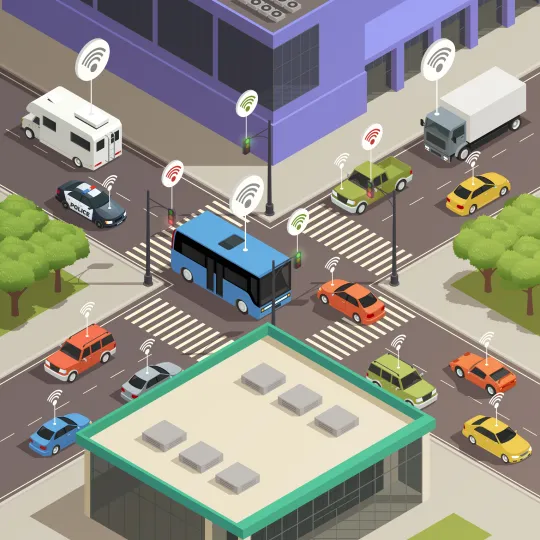
Self-driving cars can communicate with each other and traffic infrastructure, optimizing traffic flow. This can reduce congestion, travel times, and fuel consumption, benefiting both individuals and the environment.
Accessibility and Mobility
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to revolutionize transportation for people with disabilities and the elderly, offering newfound mobility and independence.
Environmental Impact
Self-driving cars can be programmed to drive more efficiently, leading to reduced fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change.
Challenges and Concerns
Ethical Dilemmas
One of the most complex challenges is the ethical decision-making process of autonomous vehicles in emergency situations. How should these cars prioritize safety, and who bears the responsibility for their decisions?
Technical Challenges
Creating fully autonomous vehicles that can navigate complex and unpredictable real-world scenarios is a formidable technical challenge that engineers and AI developers are working tirelessly to overcome.
Legal and Regulatory Hurdles
The legal and regulatory framework surrounding autonomous vehicles is still evolving, with questions about liability and safety standards yet to be fully addressed.
Public Acceptance
Building public trust and acceptance is crucial for the widespread adoption of self-driving cars. Many individuals remain skeptical or apprehensive about handing over control to machines.
Leading Companies and Their Efforts

Major Players
The development of self-driving cars has attracted some of the biggest names in the automotive and technology industries. Here are some major players actively involved in shaping the autonomous vehicle landscape:
Tesla: Known for its cutting-edge electric cars, Tesla has taken a bold step with its “Autopilot” feature. While not fully autonomous, it offers advanced driver-assistance capabilities, including adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assistance. Tesla cars are equipped with the necessary hardware for full self-driving (FSD), and the company continually updates its software to inch closer to that goal.
Waymo: A subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. (Google’s parent company), Waymo has been at the forefront of autonomous driving technology. The company started as the Google Self-Driving Car Project and has since evolved into a leader in the field. Waymo operates fully autonomous ride-hailing services in select areas and has logged millions of real-world autonomous miles.
Uber: The ride-sharing giant Uber has been heavily invested in self-driving technology. While facing setbacks, including a fatal accident in 2018, Uber continues to work on autonomous vehicles, with plans for future deployment.
General Motors (GM): Traditional automakers like GM have also jumped into the autonomous vehicle race. GM’s subsidiary, Cruise Automation, is focused on developing self-driving technology. The company has unveiled plans for a commercial autonomous vehicle service.
Ford: Ford is another traditional automaker with significant interest in self-driving cars. The company is partnering with Argo AI, a startup specializing in autonomous vehicle software, to develop self-driving technology.
Recent Developments
These major players have achieved notable milestones in recent years:
Tesla’s Autopilot: Tesla’s “Autopilot” system, though not fully autonomous, offers impressive features like adaptive cruise control, automatic lane changes, and even the capability to navigate on-ramps and off-ramps on its own. Tesla continues to refine and expand these features through over-the-air software updates.
Waymo’s Fully Autonomous Service: Waymo has introduced fully autonomous ride-hailing services in parts of Arizona, allowing passengers to experience truly driverless transportation. The company has also expanded its testing and partnerships with automakers.
Competition and Collaboration
The race to develop self-driving cars is undoubtedly fierce, with numerous companies vying for supremacy. However, what’s interesting is that amid this fierce competition, there’s also a spirit of collaboration within the industry. Here’s a closer look at this dynamic:
Competition
Technological Advancement: Companies are in a relentless pursuit of technological advancement. Each strives to outdo the other in terms of developing more sophisticated sensors, better AI algorithms, and safer autonomous driving systems. This competitive spirit drives innovation, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in self-driving technology.
Market Dominance: Many companies aim to establish themselves as dominant players in the emerging self-driving car market. Whether it’s traditional automakers like GM or tech giants like Waymo, they’re all looking to secure a significant market share and shape the future of mobility.
Consumer Trust: Building trust among consumers is vital. Companies compete not only in technology but also in demonstrating the safety and reliability of their autonomous systems. Gaining consumer confidence is a key battleground.
Collaboration
Safety First: Safety is a paramount concern in autonomous driving. Companies recognize that sharing information on safety standards and best practices benefits everyone. Collaboration in this area helps establish a baseline for safety that can be universally adopted.
Common Standards: There is a growing effort to develop common industry standards for self-driving technology. These standards aim to ensure interoperability, compatibility, and consistency in autonomous systems. Companies collaborate to define these standards, which can include protocols for data sharing, sensor technology, and more.
Data Sharing: The sheer volume of data required to train AI algorithms for self-driving is immense. Collaboration allows companies to pool anonymized data, which can be invaluable for refining AI systems and improving safety.
Regulatory Engagement: Collaboration extends to engaging with regulators and policymakers. Companies often work together to help shape the legal framework for self-driving cars, ensuring that regulations are both effective and conducive to innovation.
Alliances: Various alliances and consortia have formed to foster collaboration in the self-driving car industry. One prominent example is the Self-Driving Coalition for Safer Streets, which brings together companies like Ford, Waymo, and Volvo to work on autonomous vehicle policy and regulation.
Real-World Applications
Current Use Cases
Self-driving cars are already on the roads, primarily in the form of autonomous ride-sharing services. Companies like Uber have integrated self-driving vehicles into their fleets, allowing passengers to experience autonomous rides in select cities. Additionally, delivery services are adopting autonomous technology. Amazon, for instance, has been experimenting with autonomous delivery vehicles in various locations.
Future Applications
The future of self-driving cars extends far beyond ride-sharing and delivery. These vehicles hold the potential to revolutionize various sectors, including public transportation, logistics, and urban planning. Here’s a glimpse into their future applications:
Public Transportation: Self-driving buses and shuttles could offer efficient, on-demand transit services, reducing congestion, and improving access to public transport.
Logistics: Autonomous trucks have the potential to transform the shipping industry, making freight transportation safer and more cost-effective.
Urban Planning: Cities may redesign their infrastructure with self-driving cars in mind, leading to smarter, more efficient urban spaces. Parking lots and lanes might become obsolete, replaced by green spaces and pedestrian zones.
Accessibility: Self-driving cars could provide newfound mobility for the elderly and disabled, granting them greater independence and access to essential services.
Reduced Traffic: With improved traffic management and reduced human error, self-driving cars could significantly reduce traffic congestion, leading to shorter commutes and less time spent on the road.
Energy Efficiency: Autonomous vehicles could be programmed to optimize routes and driving behaviors, leading to reduced fuel consumption and a smaller carbon footprint.
Safety: As self-driving technology continues to evolve, the potential for fewer accidents and improved road safety is a promising prospect.
Government Regulations
Current State of Regulations
Government agencies are actively developing regulations for autonomous vehicles, balancing innovation with public safety.
Government Initiatives
Various governments have launched initiatives to promote self-driving cars, including funding for research and infrastructure development.
International Standards
The development of international standards is essential to ensure compatibility and safety across borders.
The Road Ahead
Predictions for the Future
Experts predict that self-driving cars will become increasingly common on our roads, fundamentally changing the way we think about transportation.
Technological Advancements
As self-driving cars advance, so does technology. From sensors to AI, it’s evolving rapidly. Innovations in infotainment, like iOS 17’s ten new features, enhance the journey. Discover more in our article: ‘iOS 17 Apple CarPlay’s New Features.
Societal Impacts
Self-driving cars have the potential to reshape urban planning, reduce traffic accidents, and provide newfound mobility to underserved populations.
Conclusion
As self-driving cars transition from a futuristic concept to a tangible reality, the world eagerly anticipates their widespread adoption. With the promise of enhanced safety, reduced congestion, and newfound accessibility, autonomous vehicles are poised to become the next big thing in technology.