Supernovas are the most powerful explosions in the universe. They occur when massive stars at the end of their lives collapse and explode. Supernovae release enormous amounts of energy and material, which can have a profound impact on galaxies and the universe as a whole.
Supernovae are important for a number of reasons. They enrich the interstellar medium with heavy elements, trigger the formation of new stars and galaxies, regulate the growth of galaxies, and create new opportunities for life.
Table of Contents
How Supernovas Enrich the Interstellar Medium with Heavy Elements
Stars are made up of light elements, such as hydrogen and helium. As stars fuse these elements together to produce energy, they eventually create heavier elements, such as iron, gold, and uranium. However, stars cannot fuse the heaviest elements together. When a massive star explodes as a supernova, it fuses the heaviest elements together and releases them into space.
The heavy elements released by supernovae are essential for the formation of planets and stars. Planets are made up of a variety of elements, including heavy elements. Stars also need heavy elements to form. Without supernovas, there would be no planets or stars in the universe.
How Supernovas Trigger the Formation of New Stars and Galaxies
Supernovae can trigger the formation of new stars and galaxies in a number of ways. First, supernova shockwaves can compress gas clouds, causing them to collapse and form new stars. Second, supernovae can eject material into space, which can eventually form new galaxies.
Supernovae are thought to have played a key role in the formation of the early universe. The first stars in the universe were very massive and short-lived. When these stars exploded as supernovae, they enriched the interstellar medium with heavy elements and triggered the formation of new stars and galaxies.
How Supernovas Regulate the Growth of Galaxies
Supernova explosions can remove gas from galaxies, which prevents them from growing too large. Supernova shockwaves can also heat up the gas in galaxies, which makes it more difficult for new stars to form.
The regulation of the growth of galaxies by supernovae is important for a number of reasons. First, it helps to prevent galaxies from becoming too large and collapsing under their own gravity. Second, it ensures that galaxies have a steady supply of gas to form new stars.
The Role of White Dwarfs and Black Holes in Supernovae
Type Ia supernovae typically arise in binary star systems featuring a white dwarf as one component. The white dwarf accumulates mass from its companion star until it hits a critical mass known as the Chandrasekhar limit, resulting in a supernova. This occurs when the white dwarf can no longer support its own weight, ejecting its outer layers and collapsing its inner core into a neutron star or black hole.
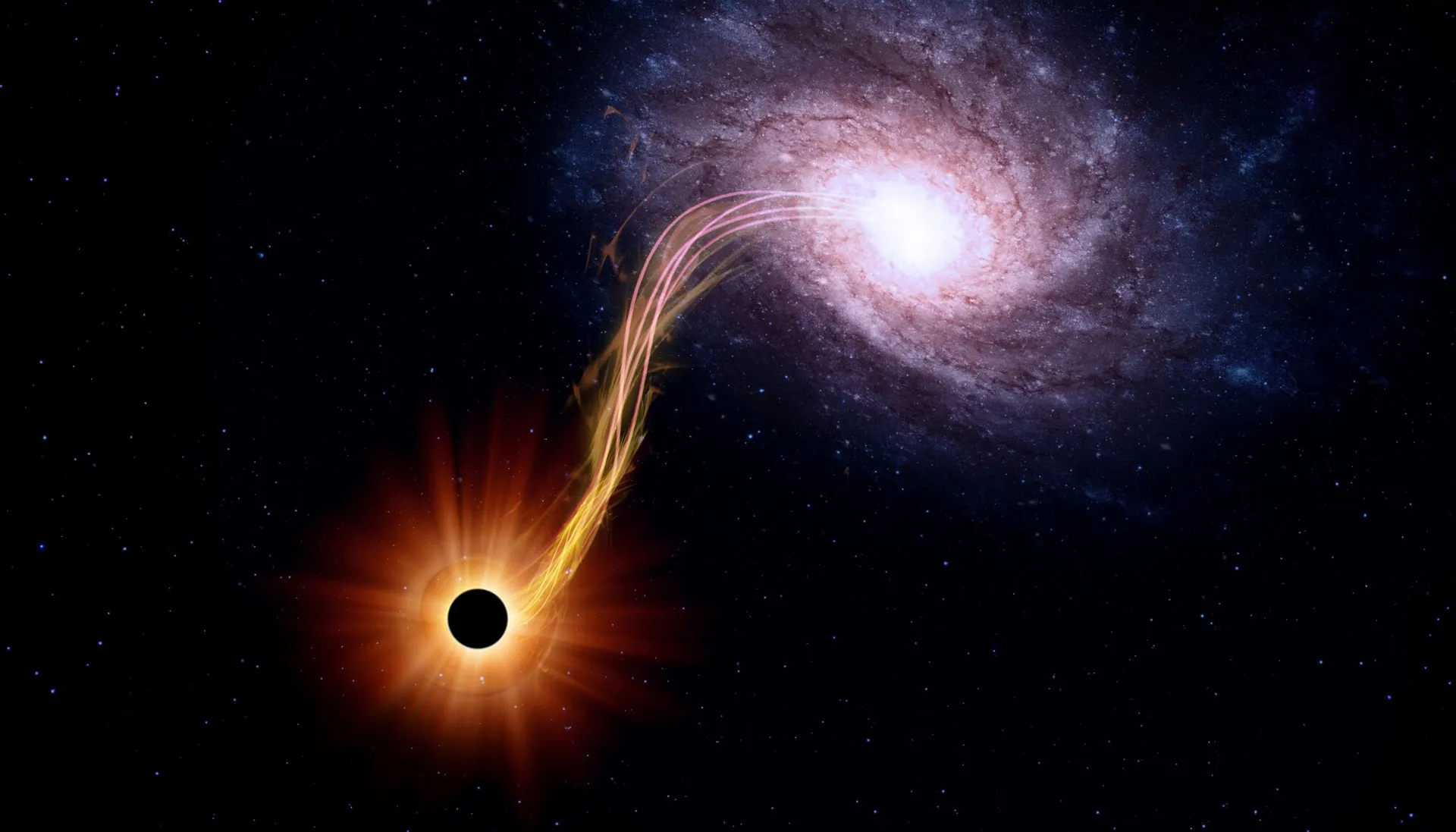

Core-collapse supernovae, on the other hand, are products of massive stars, usually at least eight times the mass of the Sun, depleting their nuclear fuel. The star’s core implodes under its gravitational forces, generating a shockwave that expels the outer layers. The core subsequently compresses to form a neutron star or potentially a black hole, depending on its mass.
Supernovae associated with black holes are less common but can occur in various ways. One scenario is the merger of a white dwarf and a black hole, where the latter’s immense gravity shreds the white dwarf, triggering a supernova. Alternatively, a black hole can induce a supernova if it accretes an excessive amount of mass, causing rapid rotation and ensuing friction. These black hole-related supernovae release substantial material into space, enriching the interstellar medium with crucial heavy elements essential for future star and planet formation.
How Supernovas Create New Opportunities for Life
Supernovas create new opportunities for life in a number of ways. First, they enrich the interstellar medium with heavy elements, which are essential for the formation of life. Second, supernovae can create new planets and star systems, which could potentially harbor life.
For example, the Earth is thought to have formed from the debris of a supernova explosion. The supernova explosion that created the Earth enriched the solar system with heavy elements, such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. These elements are essential for life on Earth.
Future of Supernova Research
Astronomers are continuing to study supernovae to learn more about how they work and how they impact galaxies and the universe. New telescopes, such as the James Webb Space Telescope, will allow astronomers to study supernovae in more detail than ever before.

Astronomers are also hoping to learn more about the role of supernovae in the formation of life. They are searching for planets that have been enriched by supernova explosions and for signs of life on these planets.
Supernovae are a fascinating and important topic of research. Astronomers are eager to learn more about these powerful explosions and their role in the universe.
Conclusion
Supernovae are one of the most important forces in the universe. They enrich the interstellar medium with heavy elements, trigger the formation of new stars and galaxies, regulate the growth of galaxies, and create new opportunities for life.
Supernovae play a vital role in the evolution of the universe. Without supernovae, there would be no planets, stars, or galaxies. Supernovae are also essential for the formation of life.