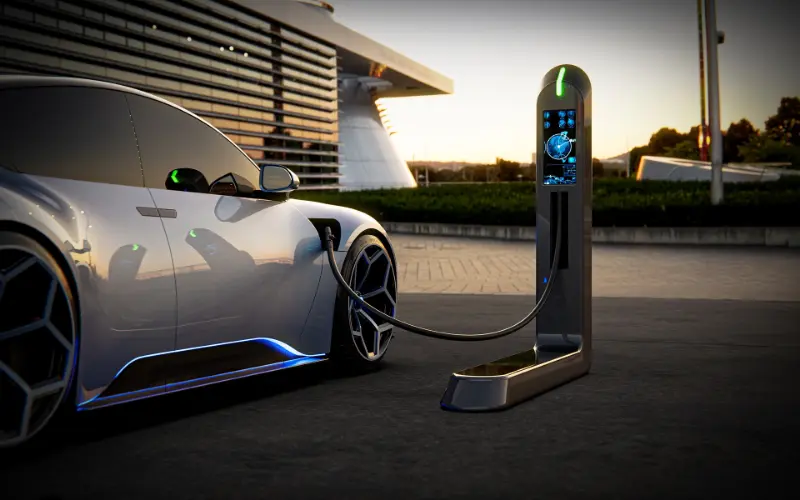
Have you ever wondered how electric vehicles (EVs) work? Well, you’re not alone. EVs are becoming increasingly popular, but many people still don’t understand how they operate. In this blog post, we’ll take a deep dive into the world of EVs and unravel the science behind their operation. From batteries to motors to controllers, we’ll explore all the essential components that make EVs tick. So, grab your curiosity and join us on this electrifying journey!
Table of Contents
What are the basics of electric vehicles?
Understanding how electric vehicles (EVs) work unveils a fascinating world of innovation. Unlike traditional gas-powered cars, EVs run on electricity, offering a clean and eco-friendly mode of transportation. Central to the EV’s functionality is its battery pack—a powerhouse storing electrical energy. This feature not only fuels the vehicle but also marks a significant leap towards a greener planet by eliminating harmful emissions.
As you plug in your EV to charge, the battery pack becomes a reservoir, storing up electrical energy that fuels the electric motor. This motor, a pivotal component in the EV’s anatomy, efficiently converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, turning the wheels and propelling the vehicle forward. This simple yet revolutionary process not only delivers a smooth driving experience but also contributes to reducing our carbon footprint.
How do electric batteries power vehicles?
Batteries are the heartbeat of electric vehicles (EVs), essential for their smooth operation. Diving into the world of EV batteries reveals diverse types, each with unique strengths. Among these, lithium-ion batteries reign supreme in the EV realm. Their popularity stems from attributes like high energy density, long lifespan, and consistent power delivery.
Understanding an EV battery involves considering its capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This measurement essentially tells us how much electrical energy the battery can store. The battery’s capacity directly influences the EV’s range—the distance it can travel on a single charge. Additionally, factors like the battery’s size and chemistry play a role in determining its charging time. This spans from a few hours to several minutes, depending on the chosen charging method.
What role do electric motors play in EVs?
Electric motors, the unsung heroes of electric vehicles (EVs), hold the key to their remarkable efficiency. These motors play a pivotal role by translating electrical energy into the mechanical power needed to set the wheels in motion. Unlike their gasoline counterparts, electric motors boast an impressive efficiency rate, converting over 77% of electrical energy into forward momentum. This is a significant leap compared to the 12-30% efficiency range typical for gasoline engines.
Delving deeper, we discover two primary types of electric motors propelling EVs: direct current (DC) motors and alternating current (AC) motors. DC motors, known for simplicity and cost-effectiveness, are commonly found in EVs. On the other hand, AC motors, offering higher efficiency and power density, stand out for their performance prowess.
How do electronic controllers function as the brains of EVs?
The electronic controller serves as the intelligent maestro, conducting a harmonious symphony of components to ensure seamless operation. Also referred to as the powertrain control module (PCM), this controller assumes a crucial role in regulating the flow of electricity among the battery, motor, and other vital components, guaranteeing peak performance and efficiency.
Picture the electronic controller as a vigilant overseer, continuously monitoring essential factors like battery voltage, motor temperature, and driver input. Its ability to make real-time adjustments based on these variables ensures a driving experience that is not only smooth but also responsive.
What is the process of recharging electric vehicles?
The journey of an electric vehicle (EV) isn’t just about the drive; it’s about the recharge—a critical aspect dictating the EV’s usability. EV charging systems, varying across different levels, play a pivotal role in this process by offering distinct charging speeds and capabilities.
Starting with Level 1 chargers, often found at homes, they provide a basic, slow trickle charge. Moving up, Level 2 chargers, prevalent at public charging stations, offer a more potent and faster charging experience. However, the true trailblazers in the EV charging realm are the DC fast chargers. These advanced chargers boast unparalleled speeds, capable of replenishing an EV’s battery in mere minutes. Particularly advantageous for long-distance travel, DC fast chargers alleviate range anxiety, ensuring minimal charging downtime and maximizing the convenience of electric mobility.
What innovations and challenges shape the future of EVs?
The future of electric vehicles (EVs) is like an open highway, filled with exciting possibilities and a few bumps. Imagine batteries that charge faster, last longer, and take you on more extended journeys – that’s what researchers are working on. Plus, self-driving EVs are already here but need more experiments to ensure safe driving and research to change how we get around.
There are challenges too. Ever heard of range anxiety? It’s when you worry your EV will run out of battery before finding a charging spot. We need to solve this worry to make EVs more popular. How? By improving battery tech and making more charging spots in public places.
How does the future look with the rise of electric vehicles?
Electric vehicles (EVs) aren’t just cars; they’re eco-friendly superheroes shaping a cleaner tomorrow. With less pollution, smooth rides, and a cool factor, they’re winning hearts. As EV batteries get better, charging spots multiply, and prices drop, they’re cruising towards dominating the global roads. Buckle up for a future where driving isn’t just a journey; it’s a green adventure! 🌿🚗